rarun2
Examples of using rarun2 to debug a binary
r2 -d rarun2 program=./<program_name> arg0=foo stdin=./<some_file> setenv=ENV_VAR=<value>-
Create a script file (script.rr2) with rarun2 config options
#!/usr/bin/rarun2 program=./<program_name> arg0=foo stdin=./<some_file> setenv=ENV_VAR=<value>Then run with
r2 -d rarun2 script.rr2- > 🚀 Use rarun2preloadto preload shared objects (.so) files. asciinema -
Use
stdin=./path/to/fileto send multiple stdin input -
To disable ASLR on a macho file, use
rarun2 aslr=no system=./somefileand then follow the instructions.
Preload
- You can preload r2 inside a process. This is similar to r2frida but native implementation
-
Example:
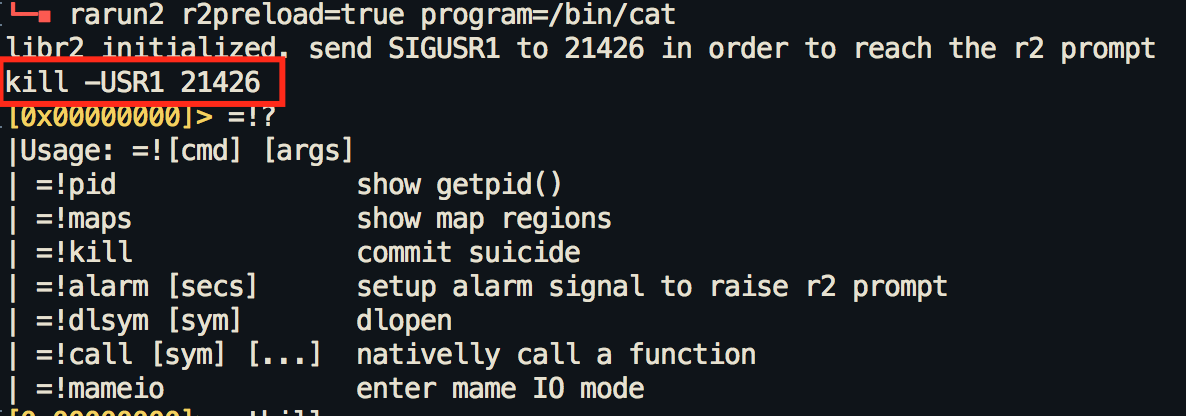
rarun2 r2preload=yes program=/bin/catfollowed by the kill command that rarun2 generates - Screenshot:
-
The red box indicates the kill command to run in another shell
-
-
Available commands inside preload are:
|Usage: =![cmd] [args] | =!pid show getpid() | =!maps show map regions | =!kill commit suicide | =!alarm [secs] setup alarm signal to raise r2 prompt | =!dlsym [sym] dlopen | =!call [sym] [...] nativelly call a function | =!mameio enter mame IO mode
-
Help
Usage: rarun2 -v|-t|script.rr2 [directive ..]
program=/bin/ls
arg1=/bin
# arg2=hello
# arg3="hello\nworld"
# arg4=:048490184058104849
# arg5=:!ragg2 -p n50 -d 10:0x8048123
# arg6=@arg.txt
# arg7=@300@ABCD # 300 chars filled with ABCD pattern
# system=r2 -
# aslr=no
setenv=FOO=BAR
# unsetenv=FOO
# clearenv=true
# envfile=environ.txt
timeout=3
# timeoutsig=SIGTERM # or 15
# connect=localhost:8080
# listen=8080
# pty=false
# fork=true
# bits=32
# pid=0
# pidfile=/tmp/foo.pid
# #sleep=0
# #maxfd=0
# #execve=false
# #maxproc=0
# #maxstack=0
# #core=false
# #stdio=blah.txt
# #stderr=foo.txt
# stdout=foo.txt
# stdin=input.txt # or !program to redirect input to another program
# input=input.txt
# chdir=/
# chroot=/mnt/chroot
# libpath=$PWD:/tmp/lib
# r2preload=yes
# preload=/lib/libfoo.so
# setuid=2000
# seteuid=2000
# setgid=2001
# setegid=2001
# nice=5
-
Example:
rarun2 stdin=somefile.txt program=/path/to/binary
rarun2 man page
RARUN2(1) BSD General Commands Manual RARUN2(1)
NAME
rarun2 — radare2 utility to run programs in exotic environments
SYNOPSIS
rarun2 [[directives]] [[script.rr2]] [[--] [program] [args]]
DESCRIPTION
This program is used as a launcher for running programs with different environment, arguments, permissions,
directories and overridden default filedescriptors.
rarun2 -t will show the terminal name and wait for a connection from another process. try rarun2 stdio=<ttypath>
program=/bin/sh
The program just accepts a single argument which is the filename of the configuration file to run the program.
It is useful when you have to run a program using long arguments or pass long data to stdin or things like that
usually required for exploiting crackmes :)
DIRECTIVES
The rr2 (rarun2) configuration file accepts the following directives, described as key=value entries and com‐
ments defined as lines starting with '#'.
arg[0-N] set value for argument N passed to the program
aslr enable or disable ASLR
bits set 32 or 64 bit (if the architecture supports it)
chdir change directory before executing the program
chroot run the program in chroot. requires some previous setup
clearenv unset the whole environment
core set no limit the core file size
connect connect stdin/stdout/stderr to a socket
pty use a pty for connection over socket (with connect/listen)
envfile set a file with lines like `var=value` to be used as env
fork used with the listen option, allow to spawn a different process for each connection. Ignored when
debugging.
input set string to be passed to the program via stdin
libpath override path where the dynamic loader will look for shared libraries
listen bound stdin/stdout/stderr to a listening socket
maxstack set the maximum size for the stack
maxproc set the maximum number of processes
maxfd set the maximum number of file descriptors
nice set the niceness level of the process
preload preload a library (not supported on Windows, only linux,osx,bsd)
program path to program to be executed
execve use execve instead of posix_spawn (osx tricks)
runlib path to the library to be executed
runlib.fcn function name to call from runlib library
r2preload preload with libr2, kill -USR1 to get an r2 shell or -USR2 to spawn a webserver in a thread
r2preweb run the webserver in a thread just at starting the r2preload
setenv set value for given environment variable
setegid set effective process group id
seteuid set effective process uid
setgid set process group id
setuid set process uid
sleep sleep for the given amount of seconds
stdin select file to read data from stdin
stdout select file to replace stdout file descriptor
system execute the given command
timeout set a timeout
timeoutsig signal to use when killing the child because the timeout happens
unsetenv unset one environment variable
VALUE PREFIXES
Every value in this configuration file can contain a special
@filename Slurp contents of file and put them inside the key
text Escape characters useful for hex chars
'string' Escape characters useful for hex chars
!cmd Run command to store the output in the variable
:102030 Parse hexpair string and store it in the variable
:!cmd Parse hexpair string from output of command and store it in the variable
%1234 Parses the input string and returns it as integer
EXAMPLES
Sample rarun2 script
$ cat foo.rr2
#!/usr/bin/rarun2
program=./pp400
arg0=10
stdin=foo.txt
chdir=/tmp
clearenv=true
setenv=EGG=eggsy
setenv=NOFUN=nogames
unsetenv=NOFUN
# EGG will be the only env variable
#chroot=.
./foo.rr2
Connecting a program to a socket
$ nc -l 9999
$ rarun2 program=/bin/ls connect=localhost:9999
Debugging a program redirecting io to another terminal
## open a new terminal and type 'tty' to get
$ tty ; clear ; sleep 999999
/dev/ttyS010
## in another terminal run r2
$ r2 -e dbg.profile=foo.rr2 -d ls
## or you can use -R option
$ r2 -R foo.rr2 -d ls
$ cat foo.rr2
#!/usr/bin/rarun2
stdio=/dev/ttys010
You can also use the -- flag to specify program and arguments in a more natural way:
$ rarun2 timeout=2 -- sleep 4
Run a library function
$ rarun2 runlib=/lib/libc-2.25.so runlib.fcn=system arg1="ls /"
SEE ALSO
radare2(1), rahash2(1), rafind2(1), rabin2(1), radiff2(1), ragg2(1), rasm2(1),
AUTHORS
Written by pancake <pancake@nopcode.org>
Feb 3, 2017
preload rarun2 pid maps kill alarm dlsym call mameio